Managing depression alone can be difficult. Find a therapist, prescriber, or both who meets your needs. Learn more
We humans are social creatures. We're so social that feeling lonely or isolated can have negative impacts on our health, causing things like depression, anxiety, stress, and high blood pressure. Conversely, having a healthy social life and support system can have a very positive impact on both your physical and mental health.
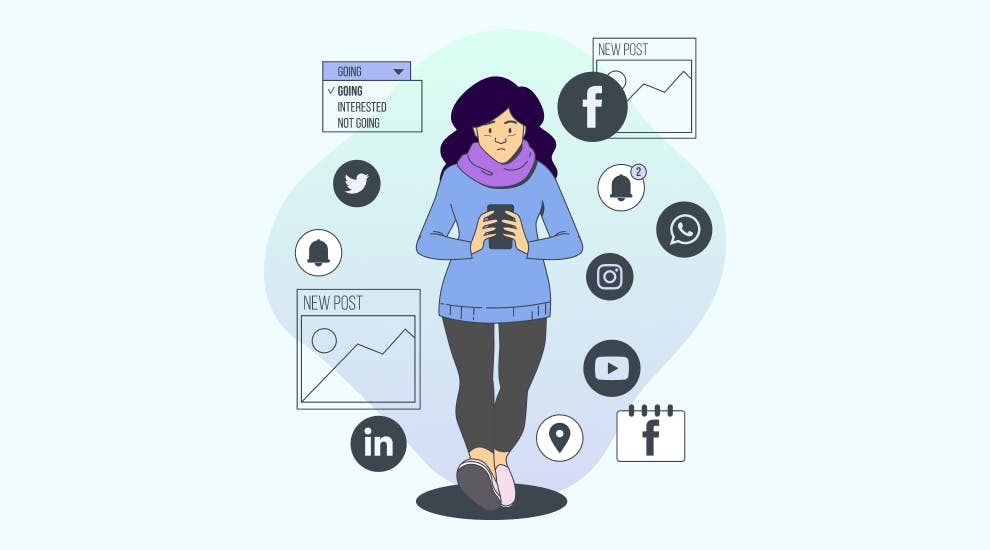
But what happens when social media takes our impulse for connection and magnifies it to a global scale?
Since we are social creatures, it makes sense that social media use has been at an all-time high during social isolation. In 2020, the average time spent on social media was 2 hours and 24 minutes per day, with people between the ages of 16-24 spending over 3 hours per day on it. That’s a huge increase from 2019, when the average time spent on social media was just over one hour per day.
Is this a bad thing? Some might argue that without social media, the pandemic might have been much more uncomfortable. While we’re stuck inside, platforms like Snapchat and Facebook have allowed us to stay connected to friends and family. And with so much more time to scroll through TikTok and Instagram, we've banded together to do things like cause significant feta cheese shortages in pursuit of the perfect pasta.
Yet, social media also exposes us to endless amounts of depressing news, triggering content, and cyberbullying. It also shows us perfectly manicured images that we might pit ourselves against every day.
So, how does all that time spent scrolling affect your mental health?
Positive and Negative Effects of Social Media
Social media has given us more opportunities for connection than ever, but it also has the power to make us feel more isolated than ever.
Positive effects of social media on mental health:
Much has been said about the harmful effects of social media on mental health, but there are plenty of positive effects as well. A recent study has suggested that routine social media use can actually contribute to social well-being and positive mental health, as long as it’s used mindfully.
For example, social media can:
- strengthen social connections by increasing opportunities for social interaction
- provide ways for people to contact and connect with one another, regardless of distance or location
- educate people on important issues by providing access to information and resources (when provided responsibly)
- build spaces for communities of people to interact with one another and express themselves
Of course, the key here is using social media mindfully.
That’s where many of us get into trouble.
Negative impacts of social media on mental health:
Studies show a link between heavy social media use and an increased risk of developing or worsening mental health issues. Today’s platforms are designed to keep users on their feeds for long periods of time. That means it’s way too easy to find yourself mindlessly consuming whatever is on your screen.
Social media companies have also been shown to maximize your usage time by promoting content that sparks outrage and other strong emotions. This “stimulating” content not only captures your attention, it leads to polarized thinking.
All of this naturally leads to excessive scrolling through social media to the point where it could interfere with your daily activities.
Effects of social media on your mental health
Symptoms of depression & anxiety. The more time you spend on social media, the higher your risk of developing symptoms of anxiety and depression. Experts point out that people with mental illnesses often use social media to distract themselves. This creates a vicious cycle where social media provides comfort while making symptoms worse.
Low self-esteem and poor self-image. It's hard to remember that everyone is putting the best version of themselves online. With so many curated posts and photoshopped images, how can you know what's real and what's fake? By comparing your unpolished life to someone's highlight reel, you may start to feel awful about yourself. Feelings of low self-esteem can surface.
Issues with sleep (insomnia). It may seem harmless to scroll through social media before you go to bed. But, if you stare at your screen for extended periods of time, you're probably exposing yourself to excessive amounts of blue light. This light interferes with melatonin production and can lead to insomnia and irregular sleep patterns.
Feelings of loneliness and isolation. Spending a ton of time on sites like Facebook, Snapchat, or Instagram can make you feel lonely and isolated, even if you’re using them to chat with your friends. According to this study, when social media is used as a substitute for real-life interaction and to escape real-life “social pain,” feelings of loneliness increase.
These are all causes for concern, but luckily there are solutions that can help you manage social media use while protecting your mental health.
How to Manage Your Relationship with Social Media
Limit your time on social media
A study found that limiting social media use to around 30 minutes per day could lead to a decrease in feelings of loneliness and depression. Even if you don't think you could reduce your time to 30 minutes, reducing your usage could have positive effects.
You can use a time tracker app to monitor how much time you spend on social media. From there, you can figure out how much of your social media time you'd like to reduce. Implement your goal by using time-limiting tools to set specific times you’re allowed to spend on social media.
Detox your newsfeed and curate positive content
If you spend every day scrolling through content that makes you angry or depressed, it's time to flex your fingers on that unfollow or hide button. Instead of engaging with accounts that make you feel awful, follow accounts and people who bring you joy. Think of it as a digital spring cleaning, a la Marie Kondo.
By looking at things that make you happy, the more likely you are to come off of social media feeling happy instead of drained.
Detox from technology and prioritize self-care
Another effective method is to detox from technology. Set a period of time aside to avoid using any devices with access to social media. If you can’t do a long detox, try a mini detox at the end of your day.
Set aside a short period of time where you are completely disconnected from technology. Take that time to practice an act of self-care. That could mean getting exercise, journaling, meditating, taking a bath, reading, or whatever else tickles your fancy.
Last, you can strengthen your commitment to detoxing by doing it with a friend. You can hold one another accountable and rely on one another for support.
Seek out mental health counseling
If you're suffering from symptoms of depression and anxiety, psychiatry and therapy could be right for you. Talking to a counselor or licensed therapist about how you feel allows you to develop healthy coping mechanisms away from a screen.
The right person can help you improve your self-esteem and learn how to make healthier choices for yourself, especially in regards to social media use. With the right care team, you can also figure out whether you need prescribed medication to combat your symptoms.
It can be intimidating to seek out treatment if you've never done it before. Luckily, Cerebral has made access to therapy, counseling, and mental health medication easier and more affordable than ever. You can now find help at the click of a button.
We're Here for You
Social media platforms are designed to be addictive, and your mental health can suffer for it. While it would be easy to tell you to just delete your social media profiles and apps, the truth is that’s an unreasonable request to make in today’s world. Instead, a balanced approach to handling social media can work wonders for your mental health and self-esteem.
If you feel like your mental health has deteriorated as a result of social media, Cerebral makes it easy for you to find the right care team to help. Our treatment plans include:
- regular assessments
- video/phone appointments
- ongoing therapy sessions
- medication delivery (if prescribed)
We believe that everyone deserves access to personalized, non-judgmental mental health care.
Medically reviewed by: David Mou, MD, MBA

Understanding and Addressing the Feelings Behind Anxiety

9 Physical Symptoms of Anxiety

The Difference Between Anxiety and Fear
If you’re having a mental
health emergency
If you're in emotional distress and
need immediate support
For National Suicide
Prevention Hotline
